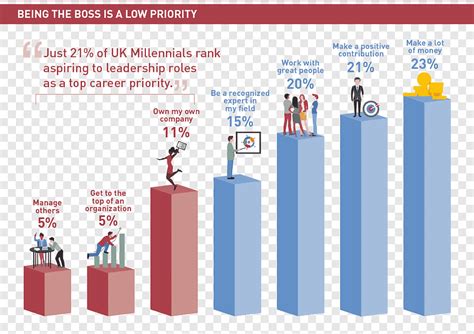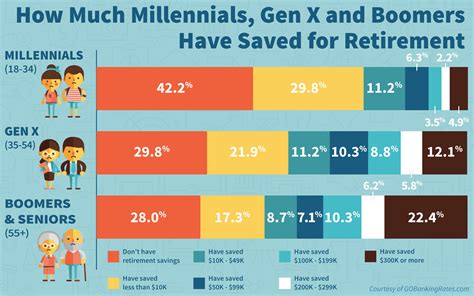
Nearly all Americans—a staggering 97%—are projected to fall short of the savings needed to retire comfortably by 2025, according to a new report highlighting the nation’s growing retirement crisis. Factors such as inflation, inadequate savings habits, and a lack of financial literacy are contributing to this bleak outlook, leaving many facing the prospect of working longer or significantly downgrading their lifestyles in retirement.
Retirement Crisis Looms as Majority Unprepared
The study paints a worrying picture for the financial futures of millions of Americans. With just months remaining until 2025, the data indicates a widespread failure to adequately prepare for retirement, potentially leading to increased financial strain and hardship for a significant portion of the population. This alarming statistic underscores the urgent need for increased financial literacy, improved savings strategies, and potential policy changes to address the systemic issues contributing to the retirement savings gap.
“Many Americans are facing a retirement savings shortfall, which means they may have to delay retirement, reduce their living expenses, or find other sources of income,” experts warn. The confluence of economic pressures and personal financial management challenges is creating a perfect storm, jeopardizing the retirement security of a vast majority of the population.
Inflation’s Impact on Retirement Savings
One of the primary drivers of this impending crisis is persistent inflation. The rising cost of goods and services erodes the purchasing power of savings, making it increasingly difficult for individuals to accumulate sufficient funds for retirement. As inflation outpaces wage growth, many Americans are forced to prioritize immediate needs over long-term savings, further exacerbating the problem.
The report highlights that “inflation has significantly impacted the ability of Americans to save for retirement, as the cost of living has increased faster than wages.” This inflationary pressure disproportionately affects lower and middle-income earners, who have less disposable income to allocate towards retirement savings. As a result, they are more likely to fall behind on their retirement goals and face a less secure financial future.
Inadequate Savings Habits and Lack of Financial Literacy
Beyond inflation, inadequate savings habits and a lack of financial literacy play a significant role in the retirement savings shortfall. Many Americans simply do not save enough, either due to a lack of awareness about the importance of retirement planning or an inability to prioritize saving amidst competing financial demands.
Financial literacy, or the understanding of basic financial concepts such as budgeting, investing, and debt management, is crucial for making informed decisions about retirement planning. However, many individuals lack the necessary knowledge and skills to effectively manage their finances and save for the future. This lack of financial literacy can lead to poor investment choices, excessive debt accumulation, and a failure to take advantage of available retirement savings opportunities.
“A lack of financial literacy can lead to poor investment choices and a failure to adequately save for retirement,” experts note. Improving financial literacy through education and awareness campaigns is essential for empowering individuals to take control of their financial futures and build a secure retirement.
The Role of Social Security and Pensions
The decline of traditional pension plans and the uncertainty surrounding the future of Social Security further contribute to the retirement savings crisis. In the past, many workers could rely on defined-benefit pension plans to provide a guaranteed income stream in retirement. However, these plans have largely been replaced by defined-contribution plans, such as 401(k)s, which place the responsibility for saving and investing on the individual.
While 401(k)s offer flexibility and potential for growth, they also require individuals to make informed investment decisions and manage their own retirement savings. This can be challenging, particularly for those who lack financial literacy or the time and resources to actively manage their investments.
Furthermore, the long-term solvency of Social Security is a growing concern. As the population ages and the ratio of workers to retirees declines, the Social Security system faces increasing financial pressure. While reforms are being considered to address these challenges, the future of Social Security remains uncertain, leaving many Americans unsure about the level of benefits they can expect to receive in retirement.
Strategies for Improving Retirement Readiness
Despite the daunting statistics, there are steps that individuals can take to improve their retirement readiness. These strategies include:
- Increasing Savings Rates: Aim to save at least 10-15% of your income for retirement, and consider increasing your savings rate gradually over time.
- Taking Advantage of Employer-Sponsored Retirement Plans: Participate in your employer’s 401(k) or other retirement plan, and take advantage of any employer matching contributions.
- Investing Wisely: Diversify your investments across different asset classes, such as stocks, bonds, and real estate, to reduce risk and maximize potential returns.
- Seeking Professional Financial Advice: Consult with a qualified financial advisor to develop a personalized retirement plan and receive guidance on investment decisions.
- Delaying Retirement: If possible, consider working a few years longer to increase your savings and reduce the length of your retirement.
- Downsizing or Reducing Expenses: Consider downsizing your home or reducing other expenses to free up more money for retirement savings.
- Improving Financial Literacy: Take steps to improve your financial literacy by reading books, attending workshops, or taking online courses.
- Automating Savings: Set up automatic transfers from your checking account to your retirement savings account to ensure consistent saving.
- Paying Down Debt: Reducing high-interest debt, such as credit card debt, can free up more money for retirement savings.
- Creating a Budget: Develop a budget to track your income and expenses and identify areas where you can save more.
Policy Recommendations for Addressing the Retirement Crisis
In addition to individual efforts, policy changes are needed to address the systemic issues contributing to the retirement savings crisis. These policy recommendations include:
- Expanding Access to Retirement Savings Plans: Make it easier for small businesses to offer retirement savings plans to their employees.
- Increasing the Social Security Retirement Age: Gradually increase the Social Security retirement age to reflect increasing life expectancies.
- Strengthening Financial Literacy Education: Mandate financial literacy education in schools and provide resources for adults to improve their financial knowledge.
- Protecting Social Security Benefits: Ensure the long-term solvency of Social Security by implementing reforms that maintain benefit levels and protect vulnerable populations.
- Incentivizing Retirement Savings: Offer tax incentives or other incentives to encourage individuals to save more for retirement.
- Regulating Financial Products and Services: Strengthen regulations to protect consumers from predatory financial products and services that can undermine retirement savings.
- Promoting Automatic Enrollment in Retirement Plans: Encourage employers to automatically enroll employees in retirement plans, with the option to opt out.
- Expanding Access to Affordable Healthcare: Ensure access to affordable healthcare to reduce healthcare costs in retirement.
- Addressing Income Inequality: Implement policies to reduce income inequality and ensure that more Americans have the resources to save for retirement.
- Promoting Portable Retirement Benefits: Make it easier for workers to transfer retirement savings between jobs.
The Long-Term Consequences of a Retirement Savings Shortfall
The consequences of a widespread retirement savings shortfall are far-reaching. A growing number of retirees may be forced to rely on government assistance, straining public resources. Increased financial insecurity among older adults can also lead to higher rates of poverty, homelessness, and health problems.
Furthermore, the retirement savings crisis can have a negative impact on the economy as a whole. As retirees cut back on spending, economic growth may slow down. A lack of retirement savings can also discourage entrepreneurship and innovation, as individuals may be less willing to take risks if they are worried about their financial security in retirement.
Addressing the retirement savings crisis requires a multi-faceted approach involving individual responsibility, employer initiatives, and government policies. By working together, we can ensure that more Americans have the opportunity to retire comfortably and securely.
The Impact on Different Demographic Groups
The looming retirement crisis doesn’t affect all Americans equally. Certain demographic groups are disproportionately vulnerable due to factors such as wage disparities, access to financial resources, and historical inequities.
-
Women: Women often face unique challenges in saving for retirement due to the gender pay gap and the likelihood of taking time off from work to care for children or other family members. As a result, women tend to have lower lifetime earnings and smaller retirement savings balances than men.
-
Minorities: Racial and ethnic minorities often face systemic barriers to wealth accumulation, including discrimination in housing, employment, and access to financial services. These barriers can make it more difficult for minorities to save for retirement and build a secure financial future.
-
Lower-Income Earners: Lower-income earners have less disposable income to allocate towards retirement savings, making it challenging to catch up on their retirement goals. They are also more likely to rely on Social Security as their primary source of retirement income, which may not be sufficient to cover their basic needs.
-
Self-Employed Individuals: Self-employed individuals are responsible for their own retirement savings, and they may not have access to employer-sponsored retirement plans. This can make it more difficult for them to save for retirement, particularly if their income is irregular or unpredictable.
-
Gig Workers: The growing gig economy presents new challenges for retirement savings. Gig workers often lack access to traditional employee benefits, such as retirement plans and health insurance, making it difficult for them to save for the future.
The Importance of Early Planning and Action
The earlier individuals start planning and saving for retirement, the better their chances of achieving their retirement goals. Starting early allows individuals to take advantage of the power of compounding, which can significantly increase their retirement savings over time.
Even small amounts of savings can make a big difference in the long run. By consistently saving a portion of their income, individuals can gradually build a substantial retirement nest egg.
Resources for Retirement Planning
Numerous resources are available to help individuals plan for retirement. These resources include:
- Financial Advisors: Financial advisors can provide personalized guidance on retirement planning and investment decisions.
- Retirement Planning Calculators: Retirement planning calculators can help individuals estimate how much they need to save for retirement.
- Government Agencies: Government agencies, such as the Social Security Administration and the Department of Labor, provide information on retirement benefits and planning.
- Nonprofit Organizations: Nonprofit organizations, such as the National Council on Aging and the AARP, offer resources and programs to help older adults plan for retirement.
- Online Resources: Numerous websites and online tools provide information on retirement planning and investment.
The Need for a Cultural Shift in Retirement Planning
Addressing the retirement savings crisis requires a cultural shift in how Americans think about retirement planning. Retirement planning should be viewed as a lifelong process, not just something to think about in the years leading up to retirement.
Individuals need to take a more proactive approach to managing their finances and saving for the future. This includes developing a budget, tracking expenses, and setting financial goals.
Employers also have a role to play in promoting retirement savings. Employers can offer retirement savings plans to their employees, provide financial education programs, and match employee contributions.
Government policies can also help to encourage retirement savings. These policies can include tax incentives for retirement savings, automatic enrollment in retirement plans, and financial literacy education programs.
Overcoming the Barriers to Retirement Savings
Several barriers can prevent individuals from saving for retirement. These barriers include:
- Lack of Income: Low income can make it difficult to save for retirement.
- Debt: High levels of debt can make it difficult to save for retirement.
- Lack of Financial Literacy: A lack of financial literacy can make it difficult to make informed decisions about retirement planning.
- Competing Financial Demands: Competing financial demands, such as housing, healthcare, and education, can make it difficult to save for retirement.
- Lack of Access to Retirement Savings Plans: A lack of access to retirement savings plans, particularly for small business employees and self-employed individuals, can make it difficult to save for retirement.
Overcoming these barriers requires a multi-faceted approach involving individual efforts, employer initiatives, and government policies.
Conclusion: A Call to Action for a Secure Retirement Future
The projected retirement savings shortfall of 97% of Americans by 2025 is a stark reminder of the urgent need to address the nation’s retirement crisis. While the statistics are concerning, it is not too late to take action. By increasing savings rates, improving financial literacy, and implementing supportive policies, individuals, employers, and policymakers can work together to ensure a more secure retirement future for all Americans. Ignoring this crisis will only lead to greater financial hardship and instability for millions in the years to come. The time to act is now, to reverse this alarming trend and build a more financially secure future for all.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. What is the main reason why 97% of Americans are projected to not be able to retire comfortably by 2025?
The primary reasons include a combination of factors: inflation eroding savings, inadequate savings habits, and a lack of financial literacy, hindering effective retirement planning. “Inflation has significantly impacted the ability of Americans to save for retirement, as the cost of living has increased faster than wages,” experts note.
2. How does inflation specifically impact retirement savings?
Inflation reduces the purchasing power of savings. As the cost of goods and services rises, the same amount of money buys less, making it harder to accumulate enough savings for retirement. Therefore, people who do not have enough disposable income will find it increasingly challenging to allocate funds for retirement savings.
3. What are some practical steps individuals can take to improve their retirement readiness, even with limited resources?
Individuals can increase savings rates (even small amounts can help), take full advantage of employer-sponsored retirement plans (especially matching contributions), invest wisely by diversifying, seek professional financial advice, and improve their financial literacy through available resources. Also, consider delaying retirement to add additional income and savings.
4. What role does Social Security play in the current retirement crisis, and how might changes to the system affect future retirees?
The uncertainty surrounding Social Security’s long-term solvency is a concern. With an aging population, the system faces financial pressure. Potential reforms could impact benefit levels and retirement ages, adding to the anxiety.
5. What policy changes are being suggested to address the retirement savings crisis on a broader scale?
Policy recommendations include expanding access to retirement savings plans for small businesses, increasing the Social Security retirement age, strengthening financial literacy education, protecting Social Security benefits, incentivizing retirement savings through tax breaks, and regulating financial products to protect consumers.