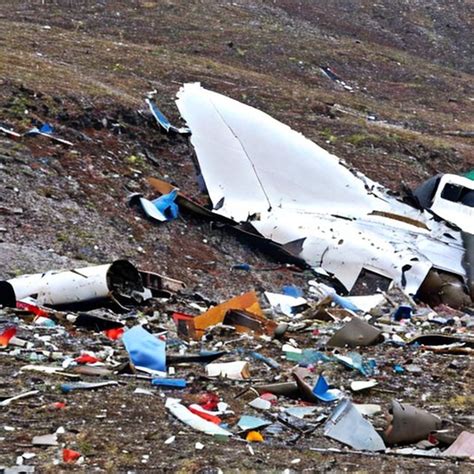
A mid-air incident involving a LATAM Airlines Boeing 787-9 Dreamliner en route from Sydney to Auckland has raised serious concerns about the aircraft’s flight control systems after what’s described as a “technical event” caused a sudden dive, injuring approximately 50 passengers. While Boeing and investigators work to determine the cause, the event has fueled renewed scrutiny of Boeing’s safety record and the reliability of its advanced aircraft technology.
The LATAM flight LA800, carrying 263 passengers and nine crew members, experienced the abrupt plunge on Monday, March 11, 2024, approximately one hour before landing in Auckland. Passengers reported being thrown from their seats, with some hitting the cabin ceiling as the aircraft violently lost altitude. “The plane just dropped. People were thrown around the cabin,” passenger Brian Jokat told the New Zealand Herald. “I’ve flown a lot, and that’s the first time I’ve ever experienced anything like that.” Reports indicated that some passengers suffered serious injuries, requiring immediate medical attention upon arrival.
The incident has prompted investigations by both the New Zealand Transport Accident Investigation Commission (TAIC) and Boeing itself. The TAIC has seized the cockpit voice recorder and flight data recorder to analyze the critical moments leading up to the event. These “black boxes” are expected to provide valuable insights into the sequence of events and any potential malfunctions. Boeing stated that it is “working to gather more information about the flight” and will provide any support needed to their customer.
Adding to the complexity, early speculation pointed towards potential interference from a seat control switch in the cockpit, but these reports are still unconfirmed and under intense investigation. The specific details of the “technical event” remain unclear, contributing to the uncertainty surrounding the long-term implications for the Boeing 787 fleet and Boeing’s overall reputation.
The Incident Unfolds
Flight LA800 departed Sydney Airport (SYD) without incident, embarking on its routine trans-Tasman journey. Approximately one hour from Auckland Airport (AKL), the situation changed drastically. Passengers described a sudden and unexpected jolt followed by a rapid descent. One passenger recounted that the experience felt as if they were free-falling.
The severity of the dive resulted in numerous injuries. Passengers who were not wearing seatbelts were particularly vulnerable, sustaining head injuries, cuts, and bruises. Medical personnel met the flight upon arrival in Auckland, providing immediate care to the injured. Thirteen individuals were hospitalized.
Following the event, LATAM released a statement confirming the incident and stating that it was “working in coordination with the corresponding authorities to support the investigations.” The airline regretted any inconvenience and expressed its commitment to the safety of its passengers and crew.
Investigation and Initial Findings
The TAIC immediately launched a comprehensive investigation, focusing on analyzing the flight data recorder and cockpit voice recorder. These devices capture critical flight parameters and cockpit audio, respectively, and are crucial for understanding the sequence of events leading up to the dive.
“We have seized the cockpit voice recorder and the flight data recorder, and we are in the process of analyzing the data,” a TAIC spokesperson said. The investigation will examine the aircraft’s maintenance history, flight crew qualifications and experience, and any potential contributing factors.
Boeing has dispatched a team of experts to assist in the investigation. In its statement, Boeing reiterated its commitment to safety and said it would “work with the New Zealand Transport Accident Investigation Commission to support their investigation.” The company’s involvement underscores the seriousness of the incident and the potential implications for the wider Boeing 787 fleet.
Adding to the mystery, early, unconfirmed reports suggested that a seat control switch issue in the cockpit may have played a role. Some reports indicated that a flight attendant may have inadvertently activated a switch while serving a meal, causing the pilot’s seat to move unexpectedly and trigger the dive. However, investigators have cautioned against drawing premature conclusions and emphasized the need for a thorough and impartial investigation.
The Boeing 787 Dreamliner: A Technological Marvel
The Boeing 787 Dreamliner is a wide-body, twin-engine jet airliner known for its fuel efficiency and advanced technology. Introduced in 2011, the 787 incorporates several innovative features, including a lightweight composite fuselage, advanced aerodynamics, and enhanced electrical systems.
The 787’s flight control system is highly sophisticated, employing fly-by-wire technology. This system replaces traditional mechanical linkages with electronic signals, offering improved control, reduced weight, and enhanced safety features. However, the complexity of fly-by-wire systems also presents potential challenges, as any malfunction or software glitch could have significant consequences.
The 787 has generally enjoyed a positive safety record since its introduction. However, there have been some past incidents involving the aircraft, including battery fires in 2013 that led to a temporary grounding of the fleet. These incidents raised concerns about the reliability of the aircraft’s electrical systems and prompted design changes.
Impact on Boeing and the Aviation Industry
The LATAM 787 incident comes at a particularly sensitive time for Boeing, which has been grappling with safety concerns and quality control issues in recent years. The two fatal crashes of the 737 MAX in 2018 and 2019, which killed 346 people, led to a worldwide grounding of the aircraft and significant reputational damage for Boeing.
Following the 737 MAX crisis, Boeing has faced increased scrutiny from regulators, lawmakers, and the public. The company has pledged to improve its safety culture and enhance its quality control processes. However, the latest incident involving the 787 raises questions about whether Boeing has fully addressed its safety issues.
The incident could have several potential consequences for Boeing and the aviation industry. It could lead to increased regulatory oversight of the 787 fleet, potentially resulting in inspections, maintenance directives, or even temporary groundings. It could also damage Boeing’s reputation further, leading to a decline in orders and market share.
More broadly, the incident underscores the importance of safety in the aviation industry and the need for continuous improvement in aircraft design, manufacturing, and maintenance. Airlines, manufacturers, and regulators must work together to ensure the safety of air travel and maintain public confidence in the aviation system.
Passenger Experiences and Aftermath
Passengers on board Flight LA800 recounted harrowing experiences, describing the chaotic scene inside the cabin during the sudden dive. Many expressed gratitude for surviving the ordeal and praised the crew for their professionalism in handling the emergency.
“It was terrifying,” said one passenger. “I thought we were going to crash.” Another passenger added, “People were screaming, and there was stuff everywhere. It was like something out of a movie.”
Following the incident, LATAM provided support to the affected passengers, including accommodation, meals, and transportation. The airline also offered counseling services to those who experienced trauma as a result of the event.
Expert Opinions and Analysis
Aviation experts have weighed in on the incident, offering insights into the potential causes and implications. Some experts have suggested that the seat control switch theory is plausible, while others have cautioned against speculating until more information is available.
“It’s possible that a seat control switch malfunction could have contributed to the incident,” said aviation safety consultant John Cox. “However, it’s important to remember that this is just one theory, and the investigation will need to consider all possible factors.”
Other experts have emphasized the importance of analyzing the flight data recorder and cockpit voice recorder to determine the precise sequence of events. “The black boxes will provide a wealth of information about what happened on board the flight,” said aviation analyst Peter Goelz. “They will help investigators understand the technical aspects of the incident and identify any potential contributing factors.”
The Future of the Investigation
The investigation into the LATAM 787 incident is expected to be lengthy and complex. Investigators will need to analyze a vast amount of data, including flight data, cockpit audio, maintenance records, and witness statements.
The investigation will also likely involve collaboration between multiple agencies, including the TAIC, Boeing, the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA), and the Chilean Civil Aviation Authority. The goal is to determine the root cause of the incident and prevent similar events from happening in the future.
As the investigation progresses, more information is expected to emerge, shedding light on the circumstances surrounding the dive and the potential implications for the Boeing 787 fleet. The findings of the investigation will be closely watched by airlines, regulators, and the public.
The Long-Term Impact
The LATAM 787 incident serves as a stark reminder of the importance of safety in the aviation industry. It highlights the potential risks associated with complex aircraft technology and the need for robust safety management systems.
The incident could have a lasting impact on Boeing, potentially affecting its reputation, financial performance, and market share. It could also lead to increased regulatory scrutiny and stricter oversight of the company’s products and processes.
More broadly, the incident underscores the need for continuous improvement in aviation safety. Airlines, manufacturers, and regulators must remain vigilant in identifying and addressing potential safety risks, and they must work together to ensure the safety of air travel for passengers around the world. The traveling public will undoubtedly be more aware and perhaps more anxious about flying until a definitive cause of the incident is determined and addressed.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
-
What happened on the LATAM flight LA800?
- Flight LA800, a Boeing 787-9 Dreamliner en route from Sydney to Auckland, experienced a sudden and unexpected dive approximately one hour before landing. This “technical event” caused passengers to be thrown around the cabin, resulting in approximately 50 injuries.
-
What is the current status of the investigation?
- The New Zealand Transport Accident Investigation Commission (TAIC) has seized the cockpit voice recorder and flight data recorder (“black boxes”) and is currently analyzing the data. Boeing is also assisting in the investigation. Early speculations about a seat control switch malfunction are being investigated, but no conclusions have been drawn.
-
What are the possible causes of the incident?
- The exact cause is still under investigation. Potential causes being explored include a malfunction in the aircraft’s flight control system, a technical issue with the aircraft’s systems, or human error. Unconfirmed reports suggest a possible issue with a seat control switch in the cockpit.
-
What is Boeing’s response to the incident?
- Boeing has stated that it is “working to gather more information about the flight” and is providing support to LATAM and the investigation. They have dispatched a team of experts to assist the TAIC in determining the cause of the incident.
-
Will this incident affect future flights on Boeing 787 aircraft?
- It is too early to say definitively. Depending on the findings of the investigation, regulatory agencies may issue safety directives, require inspections, or even temporarily ground the 787 fleet. The incident is likely to lead to increased scrutiny of Boeing’s safety protocols and the 787’s flight control systems.
Expanded Detail and Context
To further contextualize the LATAM 787 incident, it’s essential to consider the intricate landscape of modern aviation safety, the role of regulatory bodies, and the specific technologies employed in the Boeing 787 Dreamliner.
Aviation Safety Ecosystem
Aviation safety isn’t solely the responsibility of aircraft manufacturers or airlines; it’s a collaborative effort involving numerous stakeholders. These include:
- Aircraft Manufacturers: Companies like Boeing and Airbus are responsible for designing, building, and testing aircraft to meet stringent safety standards. They must continuously monitor the performance of their aircraft in service and address any potential safety issues.
- Airlines: Airlines are responsible for operating and maintaining their aircraft in accordance with safety regulations. They must ensure that their pilots and crew are properly trained and that their aircraft are regularly inspected and serviced.
- Regulatory Agencies: Agencies like the FAA (in the United States), the European Union Aviation Safety Agency (EASA), and the TAIC (in New Zealand) are responsible for setting and enforcing safety regulations. They conduct inspections, investigate accidents, and issue safety directives to ensure the safety of air travel.
- International Organizations: The International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO) is a United Nations agency that sets global standards for aviation safety, security, and efficiency.
The interplay between these entities ensures that aviation safety is continually monitored, assessed, and improved.
The Role of Fly-By-Wire Technology
The Boeing 787 Dreamliner utilizes fly-by-wire technology, which has become increasingly common in modern aircraft. Fly-by-wire systems replace traditional mechanical linkages between the pilot’s controls and the aircraft’s control surfaces (e.g., ailerons, elevators, rudder) with electronic signals.
Here’s how it works:
- Pilot Input: The pilot moves the controls (e.g., joystick or yoke).
- Sensors: Sensors detect the pilot’s control inputs.
- Computer Processing: A computer processes these inputs, taking into account factors such as airspeed, altitude, and aircraft configuration.
- Actuators: The computer sends electronic signals to actuators, which are devices that move the control surfaces.
Advantages of Fly-By-Wire:
- Improved Control: Fly-by-wire systems can provide more precise and responsive control, enhancing aircraft maneuverability and stability.
- Reduced Weight: Eliminating mechanical linkages reduces weight, leading to improved fuel efficiency.
- Enhanced Safety: Fly-by-wire systems can incorporate safety features such as flight envelope protection, which prevents the pilot from exceeding the aircraft’s structural limits.
- Simplified Maintenance: Fewer mechanical components translate to reduced maintenance requirements.
Potential Challenges:
- Software Complexity: Fly-by-wire systems rely heavily on software, which can be complex and prone to errors. Software glitches or malfunctions could potentially lead to control problems.
- Electromagnetic Interference: Fly-by-wire systems are susceptible to electromagnetic interference, which could disrupt the electronic signals and affect control.
- Power Dependence: Fly-by-wire systems require electrical power to operate. A loss of electrical power could result in a loss of control.
- Pilot Reliance: Over-reliance on automated systems and reduced “stick-and-rudder” skills among pilots can be a concern.
The Boeing 737 MAX Crashes: A Cautionary Tale
The two fatal crashes of the Boeing 737 MAX in 2018 and 2019 serve as a cautionary tale about the potential risks of complex aircraft technology and the importance of thorough safety assessments.
The crashes were attributed to a software feature called the Maneuvering Characteristics Augmentation System (MCAS), which was designed to prevent the aircraft from stalling. MCAS was triggered by faulty sensor data, causing the aircraft to repeatedly pitch nose-down, overwhelming the pilots’ ability to maintain control.
The 737 MAX crashes revealed several critical safety issues, including:
- Inadequate Pilot Training: Pilots were not adequately trained on the MCAS system, and many were unaware of its existence.
- Faulty Sensor Data: The MCAS system relied on a single angle-of-attack (AOA) sensor, which was prone to failure.
- Lack of Redundancy: There was no redundancy in the MCAS system, meaning that a single point of failure could lead to a catastrophic outcome.
- Regulatory Oversight: Concerns were raised about the FAA’s oversight of the 737 MAX certification process.
The 737 MAX crashes led to a worldwide grounding of the aircraft and significant changes to Boeing’s safety culture and quality control processes.
The Importance of Redundancy and Safety Nets
Aviation safety relies on the principle of redundancy, which means having multiple systems or components that can perform the same function. If one system fails, another system can take over, preventing a catastrophic event.
Examples of redundancy in aircraft systems include:
- Multiple Engines: Most commercial aircraft have two or more engines, so if one engine fails, the aircraft can still fly safely on the remaining engine(s).
- Multiple Flight Control Systems: Aircraft typically have multiple flight control systems, including a primary system and a backup system.
- Multiple Sensors: Aircraft have multiple sensors that measure various parameters, such as airspeed, altitude, and angle of attack. If one sensor fails, the aircraft can still rely on the other sensors.
In addition to redundancy, aviation safety also relies on a series of “safety nets,” which are designed to prevent errors from escalating into accidents. These safety nets include:
- Pilot Training: Pilots undergo extensive training to ensure that they are competent in operating the aircraft and handling emergencies.
- Standard Operating Procedures: Airlines have standard operating procedures (SOPs) that pilots must follow to ensure consistency and safety.
- Crew Resource Management (CRM): CRM is a training program that teaches pilots and crew members how to communicate effectively and work together as a team.
- Maintenance Procedures: Aircraft are regularly inspected and maintained to ensure that they are in good working order.
- Air Traffic Control: Air traffic controllers monitor aircraft movements and provide guidance to pilots to ensure safe separation.
The Future of Aviation Safety
Aviation safety is a constantly evolving field. As aircraft technology becomes more complex and air traffic volumes increase, it is essential to continue to improve safety standards and practices.
Some of the key trends in aviation safety include:
- Data Analytics: Airlines and manufacturers are using data analytics to identify potential safety risks and improve maintenance practices.
- Automation: Automation is playing an increasingly important role in aviation, but it is essential to ensure that automated systems are safe and reliable.
- Human Factors: Human factors research is helping to understand how human error can contribute to accidents and how to mitigate these risks.
- Cybersecurity: As aircraft become more connected, cybersecurity is becoming an increasingly important concern.
- Sustainable Aviation: Efforts to reduce the environmental impact of aviation are also driving safety improvements, such as the development of more fuel-efficient aircraft.
The LATAM 787 incident serves as a reminder of the ongoing challenges in aviation safety and the importance of continuous vigilance. By learning from this incident and implementing appropriate safety measures, the aviation industry can continue to make air travel safer for passengers around the world. The investigation’s findings will be critical in shaping future safety protocols and technological advancements in aviation. Understanding the nuances of fly-by-wire systems, the importance of redundancy, and the lessons learned from past incidents like the 737 MAX crashes are paramount in ensuring the continued safety and reliability of air travel.