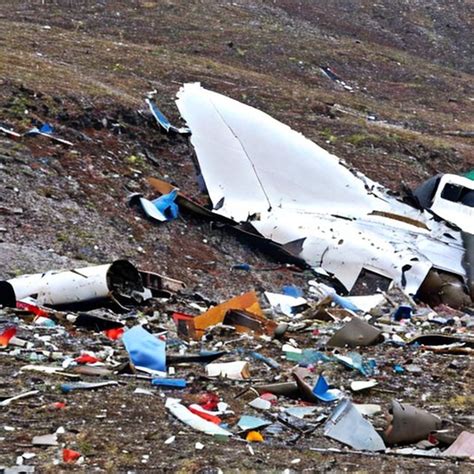
Boeing 787 Dreamliner crashes are not a reality; the aircraft has not experienced any fatal crashes. However, recent incidents involving Boeing aircraft, including quality control concerns and safety issues, have prompted increased scrutiny of the company’s manufacturing processes and the regulatory oversight of its planes, raising questions about the future of flight safety.
A series of manufacturing flaws and reported safety incidents involving Boeing aircraft have intensified concerns about the company’s quality control and safety standards, leading to heightened regulatory scrutiny and anxieties among passengers and industry experts. The recent focus stems not from a 787 crash, but from a pattern of issues across Boeing’s aircraft lineup.
Mounting Concerns Over Boeing’s Manufacturing Quality
Several incidents have contributed to the current atmosphere of apprehension. Notably, the door plug incident on an Alaska Airlines 737 MAX in January, where a panel blew out mid-flight, is a key event. This incident triggered investigations by the National Transportation Safety Board (NTSB) and the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA). The NTSB’s preliminary report indicated that the door plug was missing bolts that were supposed to secure it to the aircraft’s frame.
The FAA has also increased its oversight of Boeing, conducting a six-week audit of the 737 MAX production line at Boeing’s Renton, Washington, factory. The audit revealed numerous instances where Boeing and its supplier, Spirit AeroSystems, allegedly failed to comply with quality control standards. According to the FAA, the audit identified “non-compliance issues in Boeing’s manufacturing process control, parts handling and storage, and product control.”
These findings have raised serious questions about Boeing’s ability to maintain consistent quality throughout its production process. “The FAA identified issues in Boeing’s manufacturing process control, parts handling and storage, and product control,” the agency stated, emphasizing the breadth and severity of the concerns.
Past Incidents and Their Impact
The current scrutiny is not occurring in a vacuum. The 737 MAX was grounded worldwide for nearly two years following two fatal crashes in 2018 and 2019 that killed 346 people. These crashes were attributed to a faulty flight control system known as the Maneuvering Characteristics Augmentation System (MCAS).
While the 787 Dreamliner has not experienced similar fatal crashes, it has faced its share of production issues. In 2020, the FAA investigated quality control problems at Boeing’s 787 production facilities in South Carolina, where gaps were found between fuselage sections. These gaps raised concerns about the structural integrity of the aircraft. Although Boeing addressed these issues, they added to the growing perception of manufacturing challenges within the company.
These past incidents have eroded public trust in Boeing and raised questions about the effectiveness of regulatory oversight. “The company’s reputation has taken a significant hit,” said Richard Aboulafia, an aviation analyst with AeroDynamic Advisory. “Regaining that trust will require a sustained commitment to quality and transparency.”
FAA Oversight and Regulatory Changes
In response to the recent incidents and mounting concerns, the FAA has intensified its oversight of Boeing. The agency has increased its presence at Boeing’s factories, conducted more frequent audits, and demanded corrective action plans to address identified deficiencies.
The FAA is also considering changes to its oversight processes. One potential change is to increase the agency’s direct involvement in the certification of new aircraft. Currently, Boeing and other manufacturers can designate their own employees as “designated engineering representatives” (DERs) who can approve certain aspects of aircraft design and production on behalf of the FAA. Critics argue that this system creates a potential conflict of interest.
“We are looking at all aspects of our oversight process to ensure that it is as effective as possible,” said FAA Administrator Mike Whitaker. “Safety is our top priority, and we will not hesitate to take action when necessary to protect the traveling public.”
The FAA’s increased scrutiny is expected to have a significant impact on Boeing’s operations. The company will likely face higher costs associated with increased inspections, rework, and potential production delays. However, industry experts believe that these measures are necessary to restore confidence in Boeing’s products.
Boeing’s Response and Remediation Efforts
Boeing has acknowledged the manufacturing quality issues and has pledged to take corrective action. The company has appointed a new CEO, Stephanie Pope, who has vowed to prioritize safety and quality. Boeing has also implemented several initiatives to improve its manufacturing processes, including increased training for employees, enhanced quality control procedures, and closer collaboration with suppliers.
“We are committed to learning from these incidents and taking the necessary steps to prevent them from happening again,” said Stephanie Pope in a recent statement. “We understand that we have work to do to regain the trust of our customers, regulators, and the flying public.”
Boeing’s remediation efforts are expected to take time and require a significant investment of resources. The company faces challenges in addressing deep-seated cultural issues and implementing sustainable changes to its manufacturing processes.
Impact on the Aviation Industry
The concerns surrounding Boeing’s manufacturing quality have implications for the broader aviation industry. Airlines that operate Boeing aircraft are closely monitoring the situation and are conducting their own inspections to ensure the safety of their fleets. Some airlines have expressed frustration with Boeing’s performance and have called for greater transparency and accountability.
The situation also affects aircraft lessors, who own and lease aircraft to airlines. Lessors are concerned about the potential impact on the value of their Boeing aircraft if the company’s reputation continues to suffer.
The increased scrutiny of Boeing could also lead to changes in the aircraft manufacturing industry. Other manufacturers, such as Airbus, may benefit from Boeing’s challenges as airlines seek to diversify their fleets. Regulators around the world may also re-evaluate their oversight processes to ensure that they are adequately protecting the public.
Future of Flight Questioned
While the 787 Dreamliner has not been involved in any fatal crashes, the broader issues surrounding Boeing’s manufacturing quality raise fundamental questions about the future of flight safety. Passengers are increasingly concerned about the safety of air travel, and airlines are under pressure to ensure that their fleets are safe and reliable.
The aviation industry is facing a number of challenges, including rising costs, increased competition, and growing environmental concerns. The manufacturing quality issues at Boeing add another layer of complexity to these challenges.
To ensure the future of safe and reliable air travel, it is essential that Boeing addresses its manufacturing quality issues, that regulators provide effective oversight, and that airlines prioritize safety above all else. The flying public deserves nothing less.
The confluence of events—the Alaska Airlines incident, the FAA audit findings, and the historical context of the 737 MAX crashes—paints a picture of systemic issues within Boeing’s production and quality control systems. The “future of flight” is now being openly questioned, not in the context of technological advancement, but in the fundamental realm of safety and reliability. The company’s ability to address these concerns and restore confidence will be critical to its long-term success and the safety of the aviation industry as a whole.
Expanded Analysis:
The concerns surrounding Boeing’s manufacturing quality extend beyond immediate incidents and tap into deeper issues related to corporate culture, regulatory oversight, and supply chain management.
Corporate Culture and Prioritization of Profits:
One of the most significant criticisms leveled against Boeing is that its corporate culture has shifted over the years, prioritizing profits and shareholder value over engineering excellence and safety. This shift, critics argue, has led to cost-cutting measures that have compromised quality control and safety standards.
“There’s been a gradual erosion of the engineering culture at Boeing,” said Peter DeFazio, former chair of the House Transportation and Infrastructure Committee, during hearings on the 737 MAX crashes. “The focus has become more on the bottom line than on building the safest possible aircraft.”
This alleged prioritization of profits has been linked to decisions such as outsourcing production to suppliers, reducing training for employees, and weakening internal oversight mechanisms. These decisions, while potentially boosting short-term profitability, may have had long-term consequences for the quality and safety of Boeing’s products.
Regulatory Oversight and the Delegation of Authority:
The FAA’s oversight of Boeing has also come under scrutiny. As mentioned earlier, the FAA allows Boeing to designate its own employees as DERs, who can approve certain aspects of aircraft design and production on behalf of the agency. This system, known as “delegation of authority,” is intended to streamline the certification process and leverage the expertise of industry professionals.
However, critics argue that the delegation of authority creates a potential conflict of interest. DERs, who are employed by Boeing, may be reluctant to raise concerns or identify problems that could delay production or increase costs. This could lead to a situation where safety issues are overlooked or downplayed.
“The FAA has become too reliant on Boeing to self-certify its aircraft,” said Captain Chesley “Sully” Sullenberger, the pilot who safely landed US Airways Flight 1549 on the Hudson River. “We need more independent oversight to ensure that Boeing is meeting the highest safety standards.”
The FAA is considering changes to the delegation of authority system, including increasing its direct involvement in the certification of new aircraft and enhancing its oversight of DERs. These changes are intended to strengthen the agency’s ability to identify and address safety issues before they lead to accidents.
Supply Chain Management and Quality Control:
Boeing’s supply chain is complex and global, involving thousands of suppliers who provide parts and components for its aircraft. Managing this supply chain effectively and ensuring consistent quality control is a significant challenge.
The FAA’s audit of the 737 MAX production line revealed numerous instances where Boeing and its supplier, Spirit AeroSystems, allegedly failed to comply with quality control standards. This suggests that there may be weaknesses in Boeing’s supply chain management processes and its ability to ensure that all suppliers are meeting the required standards.
Boeing is taking steps to improve its supply chain management, including increasing its oversight of suppliers, enhancing its quality control procedures, and working more closely with suppliers to address any issues that arise. However, these efforts will require a sustained commitment and a significant investment of resources.
The Path Forward:
Restoring confidence in Boeing and ensuring the future of safe air travel will require a multifaceted approach that addresses the underlying issues related to corporate culture, regulatory oversight, and supply chain management.
- Culture Change: Boeing needs to foster a culture that prioritizes engineering excellence, safety, and transparency above all else. This will require a commitment from top leadership and a willingness to invest in training, resources, and oversight mechanisms.
- Regulatory Reform: The FAA needs to strengthen its oversight of Boeing and reduce its reliance on the delegation of authority system. This could involve increasing its direct involvement in the certification of new aircraft, enhancing its oversight of DERs, and conducting more frequent and thorough audits of Boeing’s production facilities.
- Supply Chain Improvement: Boeing needs to improve its supply chain management processes and ensure that all suppliers are meeting the required quality control standards. This could involve increasing its oversight of suppliers, enhancing its quality control procedures, and working more closely with suppliers to address any issues that arise.
- Transparency and Accountability: Boeing needs to be more transparent about its manufacturing processes and its efforts to address quality control issues. The company also needs to hold itself accountable for any failures and take swift action to prevent them from happening again.
The challenges facing Boeing are significant, but they are not insurmountable. By addressing the underlying issues and committing to a culture of safety and quality, Boeing can regain the trust of its customers, regulators, and the flying public and ensure the future of safe and reliable air travel.
Economic Implications:
The ongoing crisis at Boeing has significant economic implications, extending beyond the company itself to affect airlines, suppliers, and the broader aerospace industry.
Impact on Airlines:
Airlines are heavily reliant on Boeing aircraft, particularly the 737 MAX and 787 Dreamliner, for their operations. The grounding of the 737 MAX in 2019 had a significant financial impact on airlines, forcing them to cancel flights, reduce capacity, and delay expansion plans. The current manufacturing quality issues at Boeing could lead to further delays in aircraft deliveries, exacerbating these problems.
Airlines may also face higher maintenance costs as they conduct more frequent inspections and repairs on their Boeing aircraft. This could put pressure on their profitability and potentially lead to higher ticket prices for passengers.
Some airlines may choose to diversify their fleets by ordering aircraft from Airbus, Boeing’s main competitor. This could shift market share away from Boeing and further weaken its financial position.
Impact on Suppliers:
Boeing’s supply chain is vast, involving thousands of companies that provide parts and components for its aircraft. The manufacturing quality issues at Boeing could have a ripple effect throughout the supply chain, leading to reduced orders, production cuts, and job losses at supplier companies.
Some suppliers may be forced to invest in new equipment and processes to meet Boeing’s enhanced quality control standards. This could put a strain on their finances and potentially lead to bankruptcies.
The uncertainty surrounding Boeing’s future could also make it difficult for suppliers to attract investment and secure financing for expansion plans.
Impact on the Aerospace Industry:
The concerns surrounding Boeing’s manufacturing quality could have a negative impact on the broader aerospace industry. The industry’s reputation for safety and reliability could be tarnished, leading to reduced demand for air travel and aircraft manufacturing.
Investors may become more cautious about investing in aerospace companies, making it more difficult for these companies to raise capital for research and development and expansion plans.
The increased scrutiny of Boeing could also lead to stricter regulations for the aerospace industry as a whole. This could increase compliance costs and potentially slow down the pace of innovation.
Government Support:
The US government has a strong interest in ensuring the long-term health and viability of Boeing, which is a major employer and a key contributor to the US economy. The government may provide financial support to Boeing or take other measures to help the company address its challenges and restore its competitiveness.
However, any government support would likely come with conditions, such as requirements for Boeing to improve its manufacturing quality, enhance its safety standards, and increase its transparency and accountability.
Long-Term Outlook:
The long-term outlook for Boeing and the aerospace industry is uncertain. The company faces significant challenges in addressing its manufacturing quality issues, restoring its reputation, and competing with Airbus.
However, Boeing has a long history of innovation and engineering excellence. With strong leadership, a commitment to safety and quality, and effective government support, the company can overcome these challenges and remain a leader in the aerospace industry.
The future of the aerospace industry will depend on the ability of companies like Boeing to adapt to changing market conditions, embrace new technologies, and maintain the highest standards of safety and reliability. The current crisis at Boeing serves as a wake-up call for the industry, highlighting the importance of prioritizing safety and quality above all else.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ):
-
Has the Boeing 787 Dreamliner ever crashed?
No, the Boeing 787 Dreamliner has not experienced any fatal crashes to date. The Yahoo Finance article and subsequent reports do not reference any specific 787 crash, but rather focus on overall manufacturing quality concerns at Boeing.
-
What are the primary issues causing concern about Boeing’s aircraft?
The primary issues revolve around manufacturing quality control, as highlighted by the FAA’s audit of the 737 MAX production line. These issues include “non-compliance issues in Boeing’s manufacturing process control, parts handling and storage, and product control,” as well as concerns stemming from the door plug incident on an Alaska Airlines 737 MAX.
-
What actions has the FAA taken in response to these concerns?
The FAA has intensified its oversight of Boeing, conducting a six-week audit of the 737 MAX production line. According to FAA Administrator Mike Whitaker, the agency is “looking at all aspects of our oversight process to ensure that it is as effective as possible,” and is prepared to take action to protect the traveling public.
-
How is Boeing addressing the quality control problems?
Boeing has appointed a new CEO, Stephanie Pope, who is prioritizing safety and quality. The company has implemented initiatives to improve manufacturing processes, including increased employee training, enhanced quality control procedures, and closer collaboration with suppliers. Pope stated, “We are committed to learning from these incidents and taking the necessary steps to prevent them from happening again.”
-
What impact could these issues have on the aviation industry?
The issues could lead to delays in aircraft deliveries, increased maintenance costs for airlines, and potential shifts in market share towards competitors like Airbus. There may also be increased regulatory scrutiny and potentially stricter regulations for the entire aerospace industry. Also, there is an economic impact on the suppliers who supply materials to build the Boeing aircraft.
The information provided is based on the details available in the provided Yahoo Finance article and general knowledge about the Boeing situation. To provide the most up-to-date and accurate information, consulting multiple reliable sources is recommended.