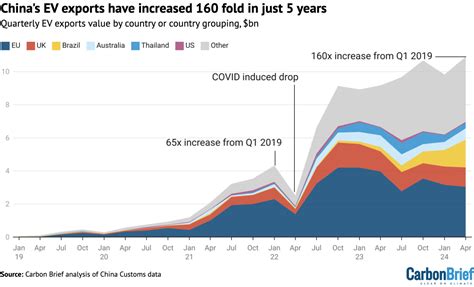
Brazil is grappling with growing trade tensions as a flood of inexpensive electric vehicles (EVs) from China rapidly penetrates its auto market, unsettling local manufacturers and prompting calls for government intervention to protect domestic industries.
Brazil’s automotive sector is facing a significant challenge as Chinese EV manufacturers aggressively expand their presence, offering vehicles at prices that local producers struggle to match. This influx of affordable EVs is reshaping the Brazilian market, sparking concerns about the long-term viability of domestic automakers and the potential impact on jobs and economic growth. The situation is prompting intense debate within the Brazilian government and industry about the need for protective measures to level the playing field.
The Chinese EV Onslaught
Chinese automakers, led by companies like BYD and GWM (Great Wall Motors), are making significant inroads into the Brazilian market. Their strategy involves offering EVs at competitive prices, often significantly lower than those of domestically produced or imported vehicles from other regions. This price advantage is driven by factors such as lower production costs in China, government subsidies for EV manufacturing, and aggressive market entry strategies.
According to the original Yahoo Finance article, “Chinese automakers are flooding Brazil with cheap EVs, threatening to upend the local auto industry.” This “flood” is not just a metaphor; it reflects the sheer volume of Chinese EVs entering the Brazilian market and their increasing market share.
The aggressive expansion of Chinese EV manufacturers is part of a broader global trend, as China seeks to become a dominant player in the EV industry. Brazil, with its large population, growing economy, and increasing environmental awareness, represents an attractive market for Chinese EV exports. However, this influx is creating friction, as local automakers struggle to compete and the Brazilian government faces pressure to protect domestic jobs and industries.
Impact on Brazilian Automakers
The surge of Chinese EVs is putting significant pressure on Brazilian automakers, who are struggling to compete on price. Brazilian manufacturers face higher production costs due to factors such as labor costs, taxes, and regulatory burdens. They also lack the economies of scale enjoyed by Chinese manufacturers, who benefit from large domestic markets and government support.
As stated in the Yahoo Finance report, the influx of inexpensive EVs “threatens to upend the local auto industry.” This is not an exaggeration. The competitive pressure from Chinese EVs could force Brazilian automakers to reduce production, cut jobs, or even close down operations.
The Brazilian Automotive Industry Association (ANFAVEA) has expressed concerns about the impact of Chinese EV imports on the domestic industry. They are calling on the government to take measures to protect local manufacturers, such as imposing tariffs or quotas on EV imports from China. ANFAVEA argues that these measures are necessary to ensure a level playing field and prevent the decline of the Brazilian auto industry.
Government Response and Policy Options
The Brazilian government is facing a difficult balancing act. On the one hand, it wants to promote the adoption of EVs and reduce carbon emissions. On the other hand, it needs to protect domestic industries and jobs.
Several policy options are being considered to address the challenge posed by Chinese EV imports. These include:
- Tariffs: Imposing tariffs on EV imports from China would increase their prices, making them less competitive with domestically produced vehicles.
- Quotas: Setting quotas on the number of EVs that can be imported from China would limit their market share and protect local manufacturers.
- Subsidies: Providing subsidies to Brazilian automakers would help them reduce their production costs and compete more effectively with Chinese EVs.
- Local Content Requirements: Requiring EV manufacturers to use a certain percentage of locally produced components would encourage investment in the Brazilian auto industry and create jobs.
- Tax Incentives: Offering tax incentives to consumers who purchase domestically produced EVs would boost demand for local vehicles.
The Brazilian government is also engaging in discussions with Chinese authorities to address the trade imbalance and seek mutually beneficial solutions. However, these discussions are likely to be complex and challenging, given the strategic importance of the EV industry to both countries.
The decision the Brazilian government makes will have far-reaching implications for the future of the country’s auto industry and its economic relationship with China.
BYD and GWM’s Strategies in Brazil
BYD and GWM are employing distinct but equally aggressive strategies to capture market share in Brazil.
- BYD: BYD, already a global EV giant, is investing heavily in Brazil. They are not just importing vehicles; they are also planning to establish local production facilities. This long-term commitment signals BYD’s confidence in the Brazilian market and its intention to become a major player in the country’s auto industry. BYD’s strategy involves offering a range of EVs, from affordable models to high-end vehicles, catering to different segments of the market.
- GWM: GWM is also investing in local production in Brazil, having acquired a former Mercedes-Benz factory. This move demonstrates GWM’s commitment to the Brazilian market and its intention to establish a strong local presence. GWM is focusing on offering competitively priced EVs, particularly in the SUV segment, which is popular in Brazil.
Both BYD and GWM are actively building their dealer networks and marketing their vehicles to Brazilian consumers. They are also investing in charging infrastructure to support the adoption of EVs. Their combined efforts are rapidly transforming the Brazilian auto market and challenging the dominance of traditional automakers.
The Broader Context: China’s Global EV Ambitions
The surge of Chinese EVs into Brazil is part of a broader global trend. China has invested heavily in the EV industry, becoming the world’s largest producer and exporter of electric vehicles. Chinese automakers are now expanding their reach into markets around the world, seeking to capitalize on the growing demand for EVs.
China’s dominance in the EV industry is driven by several factors, including:
- Government Support: The Chinese government has provided significant financial support to the EV industry, including subsidies for research and development, manufacturing, and consumer purchases.
- Large Domestic Market: China has a huge domestic market for EVs, which has allowed Chinese automakers to achieve economies of scale and reduce production costs.
- Technological Advancements: Chinese companies have made significant advancements in EV technology, particularly in battery technology, which is a key component of electric vehicles.
- Strategic Investments: Chinese companies have made strategic investments in lithium mines and other raw materials needed for EV production, ensuring a secure supply of essential components.
China’s global EV ambitions are raising concerns in other countries, including the United States and Europe, which are also seeking to develop their own EV industries. The competition between China and other countries in the EV market is likely to intensify in the coming years, with significant implications for the global auto industry.
Brazil’s Economic Ties with China
Brazil’s economic relationship with China is complex and multifaceted. China is Brazil’s largest trading partner, and trade between the two countries has grown rapidly in recent years. Brazil exports commodities such as soybeans, iron ore, and oil to China, while China exports manufactured goods such as electronics, machinery, and vehicles to Brazil.
The growing trade relationship between Brazil and China has brought significant economic benefits to both countries. However, it has also created challenges, such as trade imbalances and concerns about the impact of Chinese imports on domestic industries.
The surge of Chinese EVs into Brazil is just one example of the complex economic dynamics between the two countries. The Brazilian government needs to carefully manage its relationship with China to ensure that it benefits both countries and promotes sustainable economic growth.
The Consumer Perspective
For Brazilian consumers, the influx of affordable Chinese EVs presents both opportunities and challenges.
On the one hand, consumers now have access to a wider range of EV options at lower prices. This can make EVs more accessible to a larger segment of the population, helping to accelerate the transition to electric mobility and reduce carbon emissions.
On the other hand, consumers may have concerns about the quality and reliability of Chinese EVs. They may also be wary of purchasing vehicles from unfamiliar brands with limited service networks.
Ultimately, the success of Chinese EVs in Brazil will depend on their ability to meet the needs and expectations of Brazilian consumers. Chinese automakers need to build trust and confidence in their products by offering high-quality vehicles, reliable service, and strong warranties.
The Environmental Impact
The increasing adoption of EVs in Brazil has the potential to significantly reduce carbon emissions and improve air quality. Brazil’s electricity grid is relatively clean, with a high percentage of renewable energy sources such as hydropower. This means that EVs in Brazil have a lower carbon footprint than gasoline-powered vehicles, even when taking into account the emissions associated with electricity generation.
However, the environmental impact of EVs also depends on factors such as the source of the raw materials used to manufacture batteries and the disposal of batteries at the end of their life. It is important to ensure that the EV industry is sustainable and environmentally responsible throughout its entire value chain.
The Brazilian government is promoting the adoption of EVs through various policies, such as tax incentives and charging infrastructure development. These policies are helping to accelerate the transition to electric mobility and create a cleaner, more sustainable transportation system.
The Future of the Brazilian Auto Industry
The future of the Brazilian auto industry is uncertain. The surge of Chinese EVs is creating significant challenges for local manufacturers, but it also presents opportunities for innovation and growth.
Brazilian automakers need to adapt to the changing market conditions by investing in new technologies, improving their efficiency, and developing new products that meet the needs of Brazilian consumers. They also need to work with the government to create a level playing field and ensure that they can compete effectively with Chinese automakers.
The Brazilian government can play a key role in supporting the auto industry by providing incentives for research and development, promoting local content requirements, and investing in infrastructure. It can also work with Chinese authorities to address trade imbalances and seek mutually beneficial solutions.
Ultimately, the success of the Brazilian auto industry will depend on its ability to innovate, adapt, and compete in a rapidly changing global market.
The Role of Innovation
Innovation is crucial for the Brazilian auto industry to survive and thrive in the face of increasing competition from Chinese EV manufacturers. This innovation must occur across several fronts:
- Product Development: Brazilian automakers need to develop EVs that are specifically tailored to the needs of the Brazilian market. This includes factors such as range, price, and suitability for local driving conditions. They should also explore the use of alternative fuels, such as ethanol, which is widely available in Brazil.
- Manufacturing Processes: Brazilian automakers need to adopt more efficient manufacturing processes to reduce their production costs and compete more effectively with Chinese manufacturers. This includes investing in automation, lean manufacturing techniques, and supply chain optimization.
- Business Models: Brazilian automakers need to explore new business models, such as subscription services and shared mobility programs, to attract new customers and increase revenue.
- Partnerships: Brazilian automakers can benefit from forming partnerships with technology companies, research institutions, and other organizations to accelerate innovation and access new expertise.
The Brazilian government can support innovation in the auto industry by providing funding for research and development, creating a favorable regulatory environment, and promoting collaboration between industry, academia, and government.
The Importance of Infrastructure
The availability of charging infrastructure is a key factor in the adoption of EVs. Brazil needs to invest in a comprehensive charging network to support the growing number of EVs on its roads.
The charging network should include a mix of fast chargers and slow chargers, located in convenient locations such as shopping malls, parking garages, and workplaces. The government can play a role in incentivizing the development of charging infrastructure by providing subsidies, tax breaks, and other incentives.
In addition to charging infrastructure, Brazil also needs to invest in the electricity grid to ensure that it can handle the increased demand from EVs. This includes upgrading power plants, transmission lines, and distribution networks.
The Social Impact
The transition to EVs can have a significant social impact in Brazil. On the one hand, it can create new jobs in the EV industry, such as manufacturing, sales, and service. On the other hand, it can lead to job losses in the traditional auto industry, as production shifts to EVs.
The government needs to take steps to mitigate the negative social impacts of the transition to EVs, such as providing retraining programs for workers who lose their jobs and creating incentives for companies to hire workers from the traditional auto industry.
The transition to EVs can also improve air quality and reduce noise pollution, which can have positive health benefits for the population.
The Geopolitical Implications
The surge of Chinese EVs into Brazil has geopolitical implications, as it reflects the growing economic and technological power of China. The United States and Europe are also seeking to develop their own EV industries, and the competition between China and these countries is likely to intensify in the coming years.
The Brazilian government needs to carefully manage its relationship with China, the United States, and Europe to ensure that it benefits from the global transition to EVs. It should seek to diversify its sources of EV technology and investment and avoid becoming overly reliant on any one country.
The Legal and Regulatory Framework
The legal and regulatory framework for the EV industry in Brazil is still evolving. The government needs to develop clear and consistent regulations to promote the growth of the industry and protect consumers.
The regulations should address issues such as safety standards, charging infrastructure, battery disposal, and data privacy. They should also be designed to encourage innovation and competition.
The government should also work with other countries to harmonize regulations and standards for EVs, which can facilitate trade and reduce costs.
Conclusion
The surge of Chinese EVs into Brazil presents both challenges and opportunities for the country. While the influx threatens domestic automakers, it also offers consumers access to affordable electric vehicles and promotes a cleaner transportation system. The Brazilian government’s response will be crucial in shaping the future of the auto industry and the country’s economic relationship with China. A balanced approach that protects domestic industries while embracing innovation and sustainable technologies is essential for Brazil to navigate this complex landscape successfully. The decisions made today will have long-lasting implications for Brazil’s economy, environment, and its place in the global automotive market.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. Why are Chinese EVs so much cheaper than Brazilian-made or other imported EVs?
Chinese EVs benefit from several factors that contribute to their lower prices. These include lower production costs in China, government subsidies for EV manufacturing and exports, economies of scale due to a large domestic market, and aggressive market entry strategies. Chinese companies have also made significant advancements in battery technology, a key and expensive component of EVs, further reducing costs.
2. What measures is the Brazilian government considering to protect its domestic auto industry from the influx of Chinese EVs?
The Brazilian government is considering various policy options, including imposing tariffs on EV imports from China, setting quotas on the number of EVs that can be imported, providing subsidies to Brazilian automakers to help them reduce their production costs, implementing local content requirements for EV manufacturing, and offering tax incentives to consumers who purchase domestically produced EVs.
3. What are BYD and GWM’s plans for manufacturing EVs in Brazil?
Both BYD and GWM are planning to establish local production facilities in Brazil. BYD is investing heavily in building local factories, while GWM has already acquired a former Mercedes-Benz factory in the country. These investments demonstrate their long-term commitment to the Brazilian market and their intention to become major players in the country’s auto industry.
4. How will the increased adoption of EVs affect the environment in Brazil?
The increased adoption of EVs in Brazil has the potential to significantly reduce carbon emissions and improve air quality, especially given Brazil’s relatively clean electricity grid with a high percentage of renewable energy sources. However, the overall environmental impact also depends on the sustainable sourcing of raw materials for batteries and proper battery disposal practices.
5. What are the potential social impacts of the transition to EVs in Brazil?
The transition to EVs could create new jobs in the EV industry but may also lead to job losses in the traditional auto industry. The Brazilian government is expected to implement retraining programs for displaced workers and incentivize companies to hire workers from the traditional auto industry to mitigate these negative social impacts. The increased EV adoption could also lead to improved air quality and reduced noise pollution, benefiting public health.