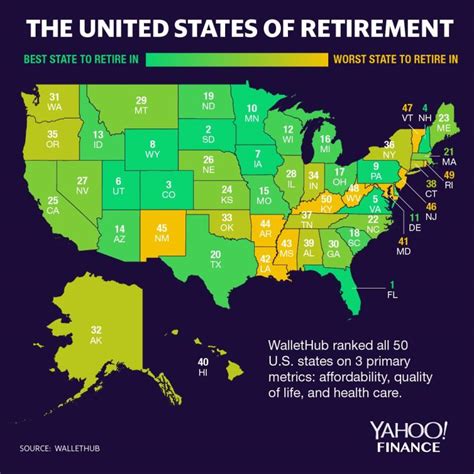
Older Americans seeking contentment might consider relocating: a recent study pinpoints the five states where seniors report the highest levels of happiness, with Hawaii topping the list. The analysis, conducted by Seniorly, a resource for senior living, considered factors like financial security, physical and mental health, community engagement, and access to quality healthcare to determine its rankings.
Hawaii Leads as the Happiest State for Seniors
Hawaii emerged as the frontrunner in Seniorly’s study, securing the top spot as the happiest state for older adults. The Aloha State excelled in multiple key categories, particularly physical health, community involvement, and overall well-being. According to Seniorly’s research, Hawaii’s “warm climate, stunning natural beauty, and strong sense of community” contribute significantly to the happiness of its senior residents. Access to quality healthcare and a focus on preventative wellness programs further bolster its appeal.
Following Hawaii: The Remaining Top Contenders
Rounding out the top five states for senior happiness are:
-
New Hampshire: Known for its low crime rates, access to excellent healthcare facilities, and focus on preventative health, New Hampshire provides a secure and healthy environment for older adults.
-
Idaho: Idaho’s appeal lies in its affordability, outdoor recreational opportunities, and close-knit communities. The state’s growing senior population enjoys a relaxed lifestyle and access to numerous activities.
-
Vermont: Characterized by its scenic landscapes, strong social connections, and emphasis on healthy living, Vermont offers a tranquil and supportive environment for seniors.
-
Massachusetts: Massachusetts provides seniors with access to world-class healthcare, numerous cultural attractions, and a wide range of senior services and programs.
Methodology: Unveiling the Factors Contributing to Senior Happiness
Seniorly’s comprehensive study employed a rigorous methodology to assess senior happiness across all 50 states. The researchers analyzed publicly available data from various sources, including the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), the U.S. Census Bureau, and the National Council on Aging (NCOA). The evaluation focused on several key pillars:
-
Financial Security: This category encompassed factors such as retirement income, cost of living, property taxes, and access to financial planning resources. States with lower costs of living and robust retirement benefits generally scored higher in this area.
-
Physical Health: Physical health indicators included life expectancy, prevalence of chronic diseases, access to healthcare services, and availability of preventative care programs. States with high-quality healthcare systems and a focus on wellness initiatives received favorable scores.
-
Mental Health: Mental well-being was assessed based on factors such as rates of depression and anxiety, access to mental health services, and the availability of social support networks. States with strong community support systems and accessible mental healthcare resources ranked higher in this category.
-
Community Engagement: Community engagement encompassed factors such as volunteer opportunities, participation in social activities, access to senior centers, and the strength of social connections. States with active senior communities and ample opportunities for social interaction received high scores.
-
Access to Quality Healthcare: This category evaluated the availability of healthcare providers, the quality of hospitals and medical facilities, access to specialized geriatric care, and the affordability of healthcare services. States with comprehensive healthcare systems and a focus on geriatric medicine scored well in this area.
By analyzing these key factors, Seniorly aimed to provide a holistic view of the elements that contribute to senior happiness and well-being.
Why Does Senior Happiness Matter?
The well-being of older adults is a critical aspect of societal health. Happy and healthy seniors are more likely to remain active and engaged in their communities, contributing their knowledge, experience, and wisdom to society. Furthermore, prioritizing senior happiness can lead to reduced healthcare costs, improved quality of life, and a more vibrant and inclusive society for all ages.
Studies have consistently shown a strong link between happiness and health in older adults. Happy seniors tend to have stronger immune systems, lower rates of chronic disease, and increased longevity. They are also more likely to maintain healthy lifestyles, engage in regular physical activity, and adhere to medical recommendations.
Implications for Policymakers and Individuals
Seniorly’s study has important implications for policymakers and individuals alike. For policymakers, the findings highlight the need to invest in programs and policies that support senior well-being, such as affordable housing, access to healthcare, transportation services, and community engagement initiatives. By prioritizing the needs of older adults, policymakers can create environments that foster happiness, health, and longevity.
For individuals, the study provides valuable insights into the factors that contribute to senior happiness. Older adults can use this information to make informed decisions about where to live, how to manage their finances, and how to prioritize their physical and mental health. By taking proactive steps to enhance their well-being, seniors can increase their chances of living long and fulfilling lives.
The Role of Community and Social Connections
The importance of community and social connections cannot be overstated when it comes to senior happiness. Studies have shown that older adults who maintain strong social networks and engage in meaningful social activities are less likely to experience loneliness, depression, and cognitive decline.
Community engagement can take many forms, from volunteering and participating in senior center activities to joining social clubs and attending cultural events. The key is to find activities that are enjoyable and provide opportunities for social interaction.
Financial Security: A Cornerstone of Senior Happiness
Financial security is another crucial factor in determining senior happiness. Older adults who have adequate retirement savings and a stable income are less likely to experience stress and anxiety related to financial matters.
Financial planning is essential for ensuring long-term financial security. Seniors should work with financial advisors to develop a retirement plan that takes into account their individual needs and goals. It is also important to explore options for managing healthcare costs and long-term care expenses.
Healthcare Access and Quality: Essential for Well-being
Access to quality healthcare is essential for maintaining the physical and mental health of older adults. Seniors should have access to a comprehensive range of healthcare services, including primary care, specialized geriatric care, and mental health services.
Preventative care is particularly important for seniors. Regular check-ups, screenings, and vaccinations can help detect health problems early and prevent them from becoming more serious.
The Impact of Lifestyle Choices on Senior Happiness
Lifestyle choices play a significant role in determining senior happiness. Older adults who maintain healthy lifestyles are more likely to experience greater levels of well-being.
Key lifestyle choices that contribute to senior happiness include:
-
Regular Physical Activity: Exercise has numerous benefits for older adults, including improved physical health, enhanced cognitive function, and reduced risk of chronic disease.
-
Healthy Diet: A nutritious diet is essential for maintaining physical and mental health. Seniors should focus on eating a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein.
-
Adequate Sleep: Getting enough sleep is crucial for overall health and well-being. Seniors should aim for 7-8 hours of sleep per night.
-
Stress Management: Stress can have a negative impact on both physical and mental health. Seniors should practice stress management techniques such as yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises.
Beyond the Top Five: Other States Showing Promise
While Seniorly’s study identified the top five happiest states for seniors, other states are also making strides in improving the well-being of their older adult populations. States like Colorado, Minnesota, and Virginia are investing in programs and policies that support senior health, financial security, and community engagement. These states offer a variety of resources and opportunities for seniors, including access to quality healthcare, affordable housing, and active senior communities.
The Future of Senior Happiness: Trends and Challenges
As the population ages, the issue of senior happiness will become increasingly important. Several trends and challenges are shaping the future of senior well-being.
One key trend is the growing demand for senior housing and long-term care services. As the number of older adults increases, there will be a greater need for affordable and accessible housing options that meet the unique needs of seniors.
Another challenge is addressing the rising cost of healthcare. Healthcare costs are a major concern for many seniors, and it is essential to find ways to make healthcare more affordable and accessible.
Conclusion: Prioritizing Senior Well-being for a Brighter Future
Seniorly’s study provides valuable insights into the factors that contribute to senior happiness. By prioritizing the well-being of older adults, we can create a more vibrant and inclusive society for all ages. Policymakers, individuals, and communities all have a role to play in ensuring that seniors have the resources and opportunities they need to live long, healthy, and fulfilling lives. The pursuit of happiness in later years is not just a personal aspiration but a societal imperative, reflecting a commitment to valuing and supporting those who have contributed so much to our world. As Seniorly’s research underscores, a holistic approach encompassing financial security, physical and mental health, community engagement, and access to quality healthcare is essential for creating environments where seniors can thrive and experience genuine well-being. By embracing this understanding, we can work towards a future where all older adults have the opportunity to live their best lives.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. What were the key factors considered in determining the happiest states for seniors?
The study conducted by Seniorly considered several factors across key categories:
- Financial Security: Assessed retirement income, cost of living, property taxes, and access to financial planning resources.
- Physical Health: Evaluated life expectancy, prevalence of chronic diseases, access to healthcare services, and preventative care programs.
- Mental Health: Examined rates of depression and anxiety, access to mental health services, and social support networks.
- Community Engagement: Measured volunteer opportunities, participation in social activities, access to senior centers, and the strength of social connections.
- Access to Quality Healthcare: Evaluated the availability of healthcare providers, the quality of hospitals and medical facilities, access to specialized geriatric care, and the affordability of healthcare services.
2. Why did Hawaii rank as the happiest state for seniors in this study?
Hawaii secured the top spot due to its high scores across several categories. The state benefits from a warm climate, stunning natural beauty, and a strong sense of community. Additionally, Hawaii boasts access to quality healthcare and a focus on preventative wellness programs, contributing to the overall well-being of its senior residents. As stated by Seniorly, Hawaii’s environment is a key factor.
3. Besides Hawaii, which other states made it to the top 5 and what are their strengths?
The other states that made it to the top 5 are:
- New Hampshire: Known for low crime rates and excellent healthcare.
- Idaho: Appreciated for its affordability and outdoor recreational opportunities.
- Vermont: Valued for its scenic landscapes and strong social connections.
- Massachusetts: Recognized for world-class healthcare and cultural attractions.
4. How can seniors use this information to improve their own well-being and happiness?
Seniors can utilize this information to:
- Consider relocating: If feasible, explore moving to a state that aligns with their priorities, such as access to healthcare, affordability, or community engagement.
- Prioritize financial planning: Ensure adequate retirement savings and explore options for managing healthcare costs.
- Engage in community activities: Participate in social events, volunteer, or join clubs to foster social connections.
- Focus on health: Maintain a healthy lifestyle through regular exercise, a balanced diet, and preventative healthcare.
- Seek mental health support: If needed, access mental health services and cultivate a strong support network.
5. What are some policy implications that can be derived from this study to enhance senior happiness across all states?
The study suggests several policy implications:
- Invest in affordable housing: Address the growing need for affordable housing options for seniors.
- Improve access to healthcare: Ensure affordable and accessible healthcare services, including specialized geriatric care.
- Promote community engagement: Support senior centers and community programs that foster social connections and engagement.
- Enhance financial security: Implement policies that support retirement savings and provide financial assistance to low-income seniors.
- Prioritize preventative care: Invest in preventative care programs to improve the physical and mental health of older adults.
Additional Deep Dive:
The Seniorly study, while highlighting the happiest states, also implicitly acknowledges the disparities in senior well-being across the nation. For every state ranked high, others face significant challenges in providing adequate support and resources to their aging populations. This necessitates a closer examination of the factors contributing to these disparities and the strategies that can be implemented to address them.
Disparities in Senior Well-being: A Closer Look
Several factors contribute to the disparities in senior well-being across different states. These include:
- Socioeconomic factors: Poverty, income inequality, and lack of access to education can significantly impact the financial security and overall well-being of seniors.
- Healthcare access and quality: Disparities in healthcare access and quality can lead to poorer health outcomes and reduced quality of life for seniors in certain states.
- Geographic location: Rural areas often lack access to essential services such as healthcare, transportation, and social support, making it more challenging for seniors to thrive.
- Cultural factors: Cultural norms and values can influence attitudes towards aging and the level of support provided to older adults.
- Policy and funding decisions: State and local policies and funding decisions can have a significant impact on the availability of resources and services for seniors.
Addressing these disparities requires a multi-faceted approach that involves:
- Investing in programs that address poverty and income inequality: This includes providing affordable housing, food assistance, and job training opportunities for low-income seniors.
- Expanding access to healthcare: This includes increasing the number of healthcare providers in underserved areas, improving access to telehealth services, and reducing healthcare costs.
- Improving transportation options: This includes providing transportation services for seniors who are unable to drive and investing in public transportation infrastructure.
- Strengthening social support networks: This includes supporting senior centers, volunteer programs, and other community-based initiatives that promote social connections.
- Advocating for policies that support seniors: This includes advocating for increased funding for senior services, policies that protect seniors from abuse and exploitation, and policies that promote age-friendly communities.
The Importance of Age-Friendly Communities
Creating age-friendly communities is essential for promoting the well-being of older adults. Age-friendly communities are designed to be inclusive and accessible to people of all ages and abilities. They offer a range of services and amenities that support the physical, social, and emotional needs of older adults.
Key features of age-friendly communities include:
- Safe and accessible streets and sidewalks: This includes well-maintained sidewalks, crosswalks with adequate lighting, and pedestrian-friendly street designs.
- Affordable and accessible housing: This includes a variety of housing options that meet the diverse needs of older adults, such as apartments, assisted living facilities, and nursing homes.
- Accessible transportation: This includes public transportation options that are easy to use and navigate, as well as transportation services for seniors who are unable to drive.
- Opportunities for social engagement: This includes senior centers, community centers, parks, and other public spaces that provide opportunities for social interaction and recreation.
- Access to healthcare and social services: This includes healthcare clinics, social service agencies, and other resources that support the health and well-being of older adults.
- Opportunities for civic participation: This includes opportunities for older adults to volunteer, participate in community decision-making, and contribute their skills and experience to society.
The Role of Technology in Enhancing Senior Well-being
Technology is playing an increasingly important role in enhancing the well-being of older adults. Technology can help seniors stay connected with family and friends, access healthcare services, manage their finances, and participate in community activities.
Examples of technology that can benefit seniors include:
- Smartphones and tablets: These devices can be used to make phone calls, send emails, access the internet, and use a variety of apps.
- Wearable devices: These devices can track activity levels, monitor vital signs, and provide alerts in case of emergencies.
- Telehealth services: These services allow seniors to consult with healthcare providers remotely, reducing the need for in-person visits.
- Online social networks: These networks can help seniors connect with others who share their interests and experiences.
- Assistive technology: This includes devices that can help seniors with disabilities perform everyday tasks, such as hearing aids, mobility aids, and adaptive equipment.
However, it is important to address the digital divide and ensure that all seniors have access to technology and the skills they need to use it effectively. This includes providing digital literacy training, affordable internet access, and technical support.
Long-Term Care: Planning for the Future
Planning for long-term care is an important aspect of ensuring senior well-being. Long-term care refers to the range of services and supports needed by individuals who are unable to care for themselves due to age, disability, or illness.
Long-term care services can be provided in a variety of settings, including:
- Home: Home care services can provide assistance with activities of daily living, such as bathing, dressing, and eating.
- Assisted living facilities: Assisted living facilities provide housing, meals, and personal care services for seniors who need assistance with some activities of daily living.
- Nursing homes: Nursing homes provide 24-hour medical care and support for seniors who require a high level of care.
Planning for long-term care involves:
- Assessing your needs: Determine what type of long-term care services you are likely to need in the future.
- Exploring your options: Research different long-term care facilities and services in your area.
- Developing a financial plan: Determine how you will pay for long-term care services.
- Discussing your wishes with your family: Communicate your preferences for long-term care to your family members.
The Importance of Social Inclusion and Combating Ageism
Social inclusion and combating ageism are essential for promoting the well-being of older adults. Ageism refers to the stereotypes, prejudice, and discrimination against individuals based on their age.
Ageism can manifest in many ways, including:
- Negative stereotypes: Believing that older adults are frail, incompetent, and unproductive.
- Discrimination: Denying older adults opportunities for employment, housing, and healthcare.
- Social isolation: Excluding older adults from social activities and community life.
Combating ageism requires:
- Challenging negative stereotypes: Promote positive images of aging and highlight the contributions of older adults to society.
- Promoting intergenerational connections: Encourage interactions between people of different ages to foster understanding and respect.
- Advocating for policies that protect older adults: Support policies that prohibit age discrimination and promote social inclusion.
- Raising awareness about ageism: Educate the public about the harmful effects of ageism and the importance of valuing older adults.
By creating a more inclusive and age-friendly society, we can ensure that all seniors have the opportunity to live long, healthy, and fulfilling lives. The goal isn’t just to add years to life, but life to years, making those later years a time of continued growth, contribution, and happiness.









